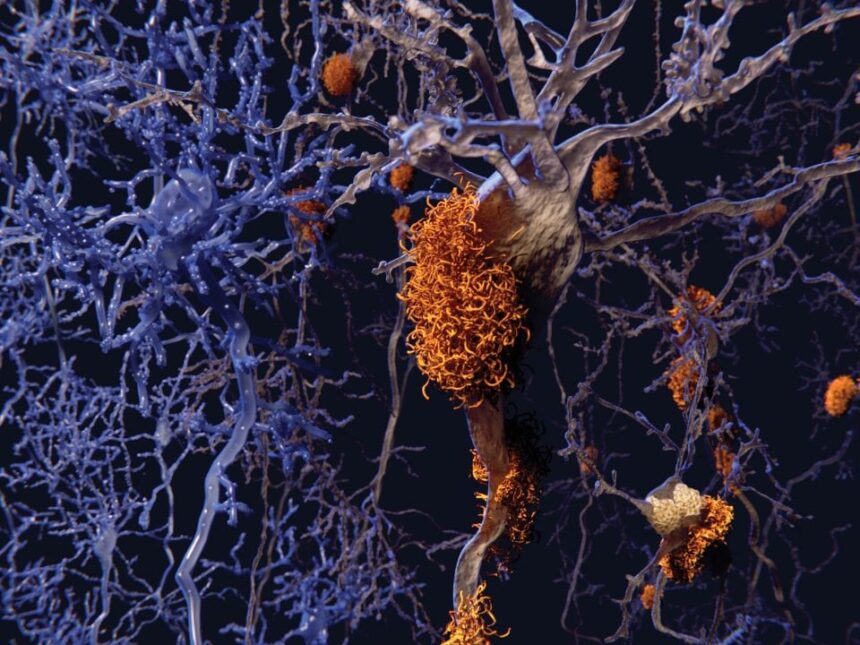
According to a study by Hokkaido University, researchers have built a new method capable of detecting build-up of amyloid beta in the brain using biomarkers found in blood samples.
Amyloid beta is a characteristics theoretically associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The research was published in Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy.
The study began by testing rodent models. A team of a researchers developed biosensing technology able to identify amyloid beta-binding exosomes in the blood of the test subjects, which increases as amyloid beta accumulates in the brain.
“In this study, immuno-digital invasive cleavage assay (idICA) was developed for quantitating target-intact extracellular vesicles (EVs),” the findings state.
“EVs were captured onto ganglioside GM1-specific cholera toxin B subunit (CTB)-conjugated magnetic beads and detected with a DNA oligonucleotide-labeled Aß antibody. Fluorescence signals for individual EVs were then counted using an invasive cleavage assay (ICA).”
“The present findings suggest that peripheral EVs harboring Aß and GM1 reflect Aß burden in mice. The idICA is a valuable tool for easy quantitative detection of EVs as an accessible biomarker for preclinical AD diagnosis,” the study’s authors wrote in their findings.