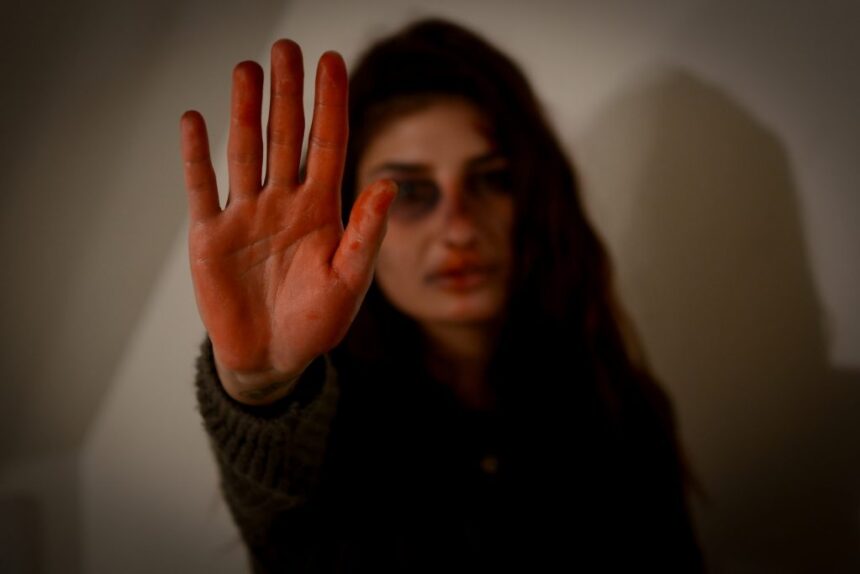
A study by McGill University has explored intimate partner violence (IPV), concluding that women who experience IPV are significantly more likely to be infected with HIV.
The study centered on women in Sub-Saharan Africa, an area of the world known to have a high prevalence of IPV and HIV cases.
The findings can be read in The Lancet HIV.
“57 surveys with data on self-reported HIV testing and past-year physical or sexual IPV were available from 30 countries, encompassing 280 259 ever-partnered women aged 15–64 years. 59 456 (21·2%) women had experienced physical or sexual IPV in the past year,” according to researchers.
“Past-year physical or sexual IPV was associated with recent HIV acquisition and less frequent viral load suppression. Preventing IPV is inherently imperative but eliminating IPV could contribute to ending the HIV epidemic.”
The research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canada Research Chairs Program, and Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé.