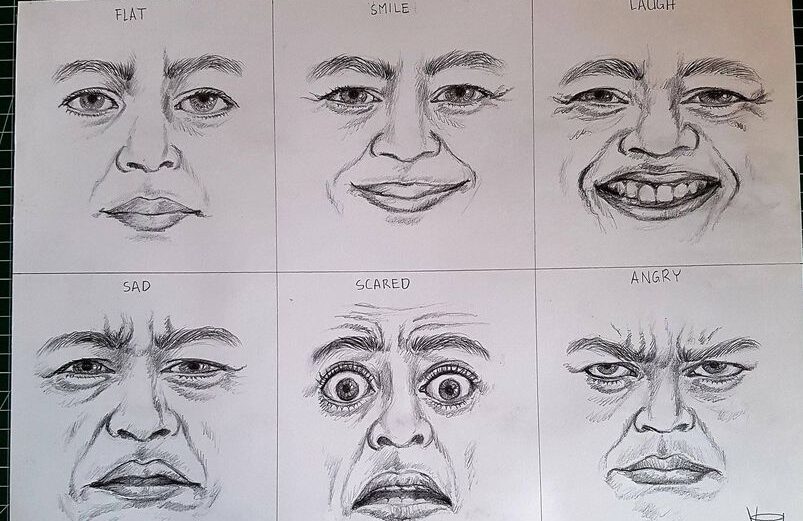
A new study carried out by a team of research sleuths at Edge Hill University found that autistic people may be better than neurotypical people at reading emotions in certain contexts.
The research was conducted in the midst of prior findings that suggested autistic people may demonstrate poorer facial emotion recognition than their neurotypical counterparts.
The findings, consisting of 196 participants, were published in Autism Research.
“To investigate this further, this work explores emotion recognition in autistic and neurotypical adults,” the study’s authors explained in the study. “Groups were compared on a standard and a cartoon version of the Reading the Mind in the Eyes test.”
“Results indicated that autistic individuals were not significantly different from neurotypicals on the standard version. However, autistic people outperformed neurotypicals on the cartoon version,” the findings also emphasized.
“The implications for these findings regarding emotion recognition deficits and the social motivation account of autism are discussed and support the view of socio-cognitive differences rather than deficits in this population.”