Published in Nature Communications, researchers at UT Southwestern showed how increasing brown fat may reduce blood sugar and provide new solutions to tackle type 2 diabetes.
“Exposure of mice or humans to cold promotes significant changes in brown adipose tissue (BAT) with respect to histology, lipid content, gene expression, and mitochondrial mass and function,” researchers explained in the news report.
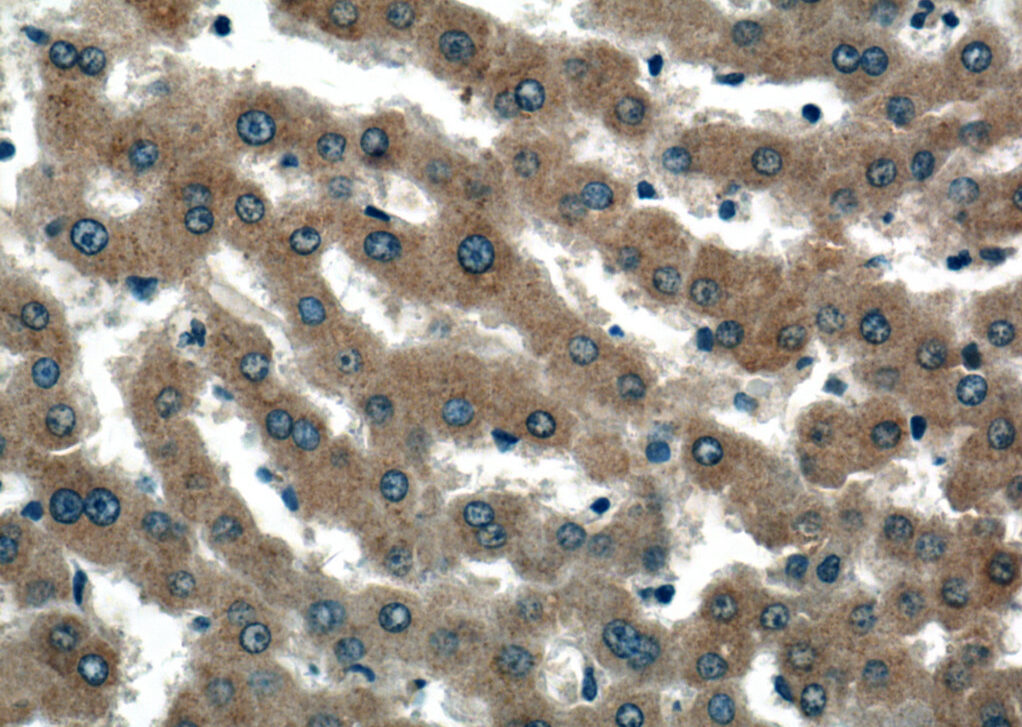
“Herein we report that the lipid droplet coat protein Perilipin 5 (PLIN5) increases markedly in BAT during exposure of mice to cold. To understand the functional significance of cold-induced PLIN5, we created and characterized gain- and loss-of-function mouse models.”
The study focused on brown adipose tissue, which has been previously examined for its potential role in weight loss.
Researchers uncovered that brown fat may be a significant contributing factor for combatting type 2 diabetes. The notion was established during their focus on a protein known as perilipin 5.
“We further show that promoting PLIN5 function in BAT is associated with healthy remodeling of subcutaneous white adipose tissue and improvements in systemic glucose tolerance and diet-induced hepatic steatosis,” researchers wrote in their journal report.
“These observations will inform future strategies that seek to exploit thermogenic adipose tissue as a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes, obesity, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.”