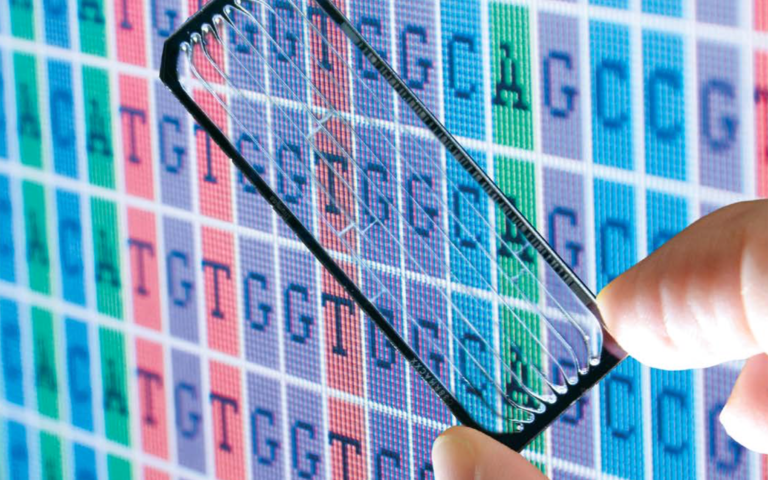
Research in Nature led by first author Federico Abascal unveiled a new method known as nanorate sequencing (NanoSeq), which showcases the capability to study genetic changes and their occurrences in human tissues.
According to researchers at Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, the new breakthrough in studying genetic changes in human tissues is a major step forward for aging.
Additionally, the research refutes the notion that cell division is the primary mechanism behind genetic changes.
“Here, to overcome these limitations, we developed nanorate sequencing (NanoSeq), a duplex sequencing protocol with error rates of less than five errors per billion base pairs in single DNA molecules from cell populations. This rate is two orders of magnitude lower than typical somatic mutation loads, enabling the study of somatic mutations in any tissue independently of clonality,” the study’s authors stated in their journal report.
“Together, our results suggest that mutational processes that are independent of cell division are important contributors to somatic mutagenesis. We anticipate that the ability to reliably detect mutations in single DNA molecules could transform our understanding of somatic mutagenesis and enable non-invasive studies on large-scale cohorts.”
The study was published online on April 28th, 2021.